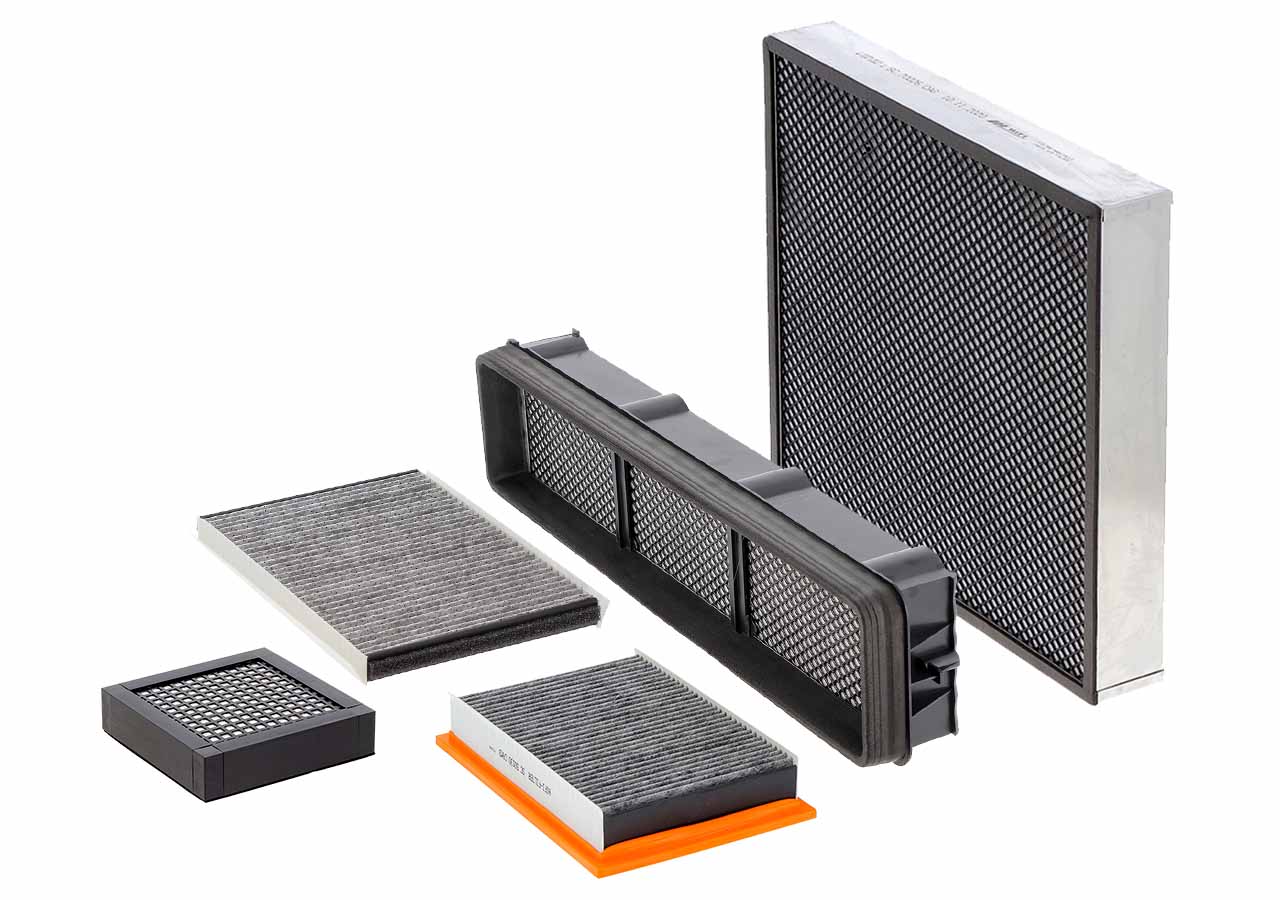
Produced in powder, granule or fibre form, activated carbon follows a
precise manufacturing method:
CarbonizationIn an oxygen-free environment, selected organic plant material (wood bark, bamboo, coconut shells, olive pits, etc.) is calcined at high temperatures. During this process, particles of carbonised material evaporate and create pores in the charcoal.
The material has become porous.
ActivationActivation removes the tar still trapped in the pores of the material. This process increases the porosity of the activated carbon and thus increases its capacity to adsorb contaminants. Thanks to this step,
the adsorption surface can be between 500 and 2500m²/g! There are two methods for this: one physical and one chemical.
- Physics: Again, the coal is carbonised at a very high temperature, while inducing a thermal shock with the help of an air stream or steam.
- Chemical: Immersed in a chemical agent (e.g. phosphoric acid), the activated carbon is heated to a lower temperature and then rinsed to remove product residues.
The difference between these two methods?
Physical activation forms narrow pores while chemical activation generates larger pores.